Gum disease (periodontal disease), out-of-the tissues that surround and support is a disease that affects not out. Never non-caries of the teeth can be lost due to this disease. Periodontal disease can affect one or many teeth; in children, Growth-age individuals, which can be seen in adults and the elderly are the most common chronic diseases in the society. Symptoms to watch hardly noticeable by the patient usually painless, and in most cases the application is a late physician.
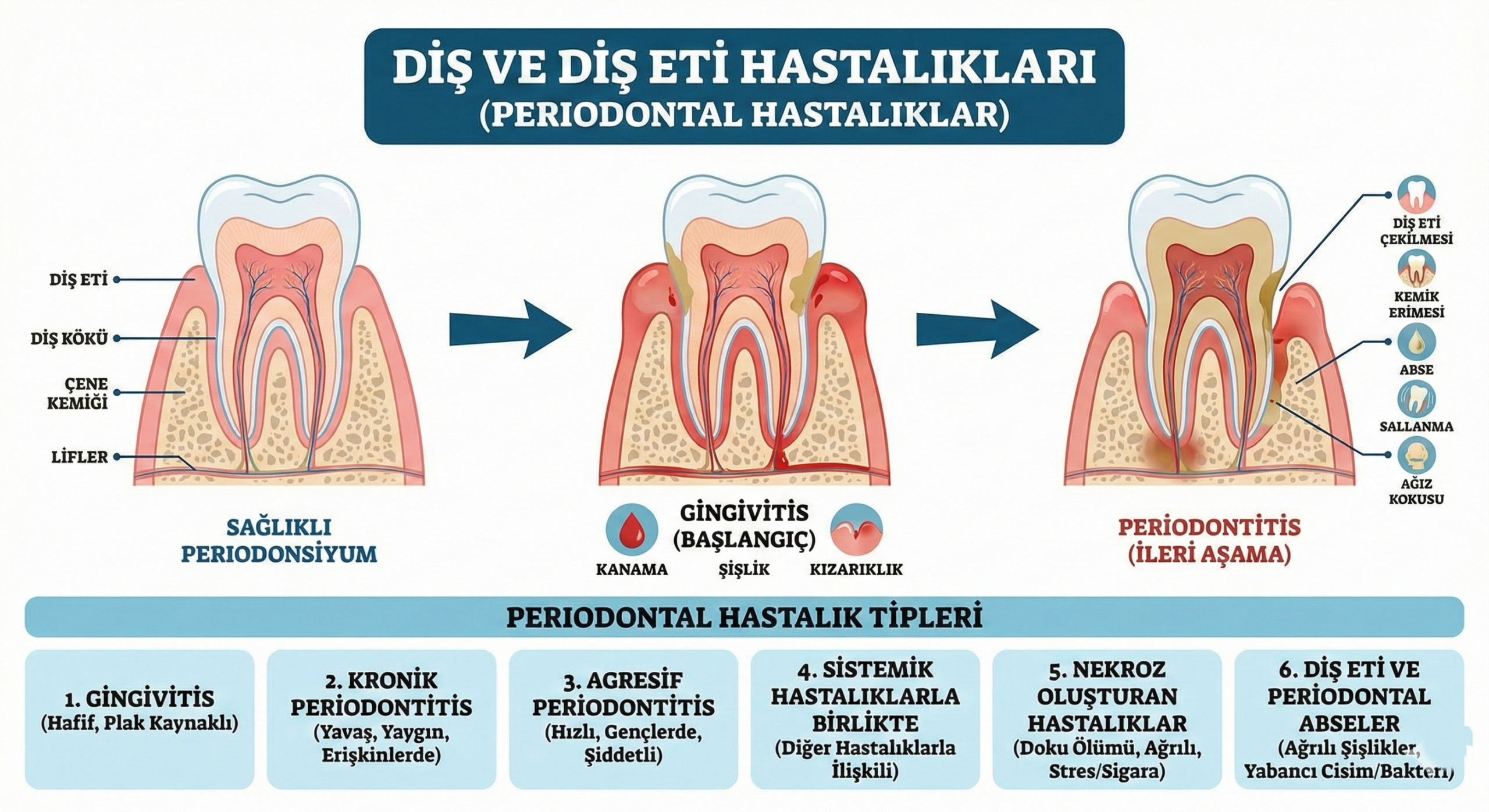
Support tissues of the external environment; gums, teeth, and the jawbone are the fiber that connects the jaw bone and the root of the tooth, and this structure “periodonsiyum” takes its name. The infection affects only the gums situations that is called “gingivitis”. Gingivitis symptoms; red, swollen, shiny, soft consistency, and is gums that bleed easily. Bleeding is the most common symptom.
In more advanced cases, your gums along with other tissues are also affected above-mentioned situations where “periodontitis” is defined as. Periodontitis symptoms; bleeding gums, red/bluish-purplish discoloration, gum recession, gum growth, displacement of teeth, aralanma, stretching, rocking, abscess formation, sensitivity, and bad breath. The pain usually is seen with abscess formation. Ultimately periodontal tissue infection, aesthetic disorder, and the loss of the implant decreased chewing carry and support infrastructure consists of a diseased to be made.
What are the types of periodontal disease?
The type of periodontal disease that affects the success of periodontal treatment is an important factor. There are many types of periodontal disease. Common ones include:


Gingivitis
A milder form of periodontal disease. Microbial dental plaque is the most important reason. Swelling of The Gums, Red color, brightness, and spontaneous bleeding during brushing or with halitosis noticeable. During this period, pain or no, or very little. Gingivitis can be treated with proper oral care and treatment. In addition, the outer flesh sinking into the bodies of acute pain and an abscess in the gum will bring.
Chronic periodontitis
Periodontitis is the most common type. The majority of individuals it is available in adult age. Progresses very slowly, and hardly noticeable symptoms are ignored by supposing late or normal. For this reason, in treatment, sometimes they may be late. Infection of the tissues supporting and surrounding the teeth destruction. Respectively, the gum, the gum and the tooth and connects to external fibers and bone that connects the root of the tooth to the bone, melt the outer cell is formed. Microbial dental plaque and calculus on the root surface at the bottom of the gums, at the same time multiplying the infection of bacteria and food debris accumulate in the mobile space and causes the reduction of the bone support of the teeth and move through the deeper tissues. Symptoms; dark red, the color of purplish gums, gum recession/growth, aralanma teeth, elongation, rotation, shaking, dysfunction, teeth and food particles into your pockets stuffed with abscess formation, mouth odor, aesthetic disorder can be listed as. Beginners and intermediate level chronic periodontitis, non-surgical methods are treated with advanced chronic periodontitis is treated with additional surgical methods. Diseases that affect the immune system and certain systemic diseases such as diabetes, stress, and factors such as smoking affects the response to treatment and the severity of chronic periodontitis.
Aggressive periodontitis
Less frequently, but more violent and young people in a way which affects the type of periodontitis. This condition may be hereditary. Systemic as healthy individuals. There are 2 types of local and common. Local clinical signs associated with gum type are minimal, but it is the next dimension of pocket depth and bone destruction. Common type in both clinical symptoms and bone loss has influenced a greater number of noticeable is at a level other than. Periodontitise more difficult than treatment of chronic and complex.
Periodontitis with systemic disease
Periodontitis; some blood diseases, metabolic diseases, genetic diseases and diseases that affect the immune system can be seen as a symptom of the mouth. The treatment is executed together with the medical doctor.
Necrosis forming periodontal diseases
Starting from the top of the triangular tooth that fills the space between the teeth and gums destruction(necrosis), which leads to osteoporosis and periodontal diseases are left untreated scroll. Smokers who are under psychological stress in patients with oral hygiene in a very bad ones, are more common in AIDS patients. Patients complain of severe pain.
Gum and periodontal abscesses absele
An abscess in the gums, teeth sinking into flesh gives rise to foreign substances. Red color in the relevant region, swelling, and tenderness. In untreated cases with osteoporosis and advanced with the increase in the number of bacteria in the periodontal pocket periodontal abscesses occur that affect deeper tissues. Pain, swelling, red – purplish color, bleeding, pus, such as the flow of signs and symptoms.